Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally existing polysaccharide of the extracellular matrix found in all animals, in their connective tissues, skin, eyes, and joint fluids. Based on its molecular weight, three divisions are made for HA: low molecular weight hyaluronic acid (LMW-HA), medium molecular weight hyaluronic acid (MMW-HA), and high molecular weight hyaluronic acid (HMW-HA). These different kinds of HA have peculiar properties that enable their use for specific applications in fields as diverse as medicine, cosmetics, ophthalmology, and nutrition. The following paper will detail important differences between HMW-HA and LMW-HA and then highlight why HMW-HA is particularly important for some applications.
Why High Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid (HMW-HA) Is Important
Superior Moisturizing Ability
One of the main characteristics of HMW-HA is that it has a high moisturizing capacity. Its large molecular structure holds much water and retains it, creating a moisture-retentive film on the surface of the skin. Such features are important in preventing transepidermal water loss, thus maintaining skin hydration and elasticity.
By contrast, LMW-HA can penetrate within the layers of the skin and work on hydration from the inside but lacks the ability to form this protective barrier at the skin’s surface. Accordingly, HMW-HA is an indispensable ingredient in products for prolonged hydration of the skin surface, such as moisturizers and masks.
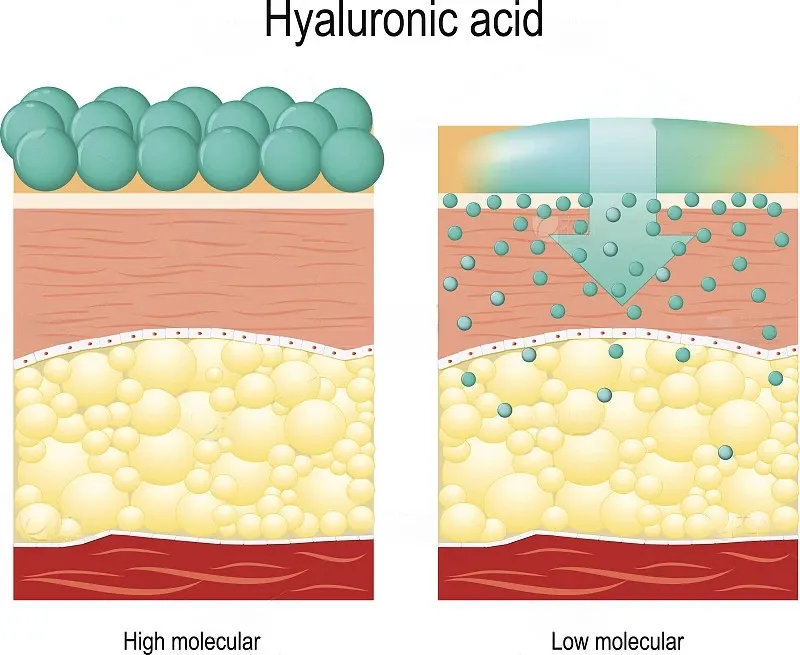
Fig 1. High vs low molecular weight hyaluronic acid
Excellent Lubricating Properties
HMW-HA acts as a lubricant within the joints and eyes, making it a material of great importance in the medical field for treating disorders in the joints and with ophthalmic solutions. Clinically, HMW-HA in intra-articular injections is indicated for treating joint conditions like osteoarthritis. In its high molecular weight and viscoelastic nature, HMW-HA is used for lubrication purposes and as a shock absorber inside the cavity of an articulating joint, thus reducing pain and improving function in the articulating joint.
Similarly, in ophthalmology, HMW-HA is applied for the preparation of artificial tears and during surgical procedures in the eye to give a long-lasting lubricating film over the ocular surface, thus protecting the vulnerable ocular tissue and facilitating undisturbed eye movement. LMW-HA may not give the same viscosity and level of protection, which therefore would limit its capability in such respect.
Outstanding Anti-inflammatory Properties
HMW-HA is known to have anti-inflammatory activity and can, therefore, help in many inflammatory conditions and thus result in tissue repair. The HMW-HA is further noted to moderate immunity, and reduce the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby mitigating overall inflammation. This makes HMW-HA an effective component in wound dressings or skin care products aimed at reducing redness and irritation.
On the other hand, due to its lower mass and corresponding size, LMW-HA is more likely to be delivered through deeper skin layers and thus may help in the regeneration of the extracellular matrix and healing at a different level. However, the overall effect on anti-inflammatory activity is weak when compared to that of HMW-HA.
Protective and Barrier Functions
HMW-HA forms a barrier on the surface of the skin that protects against environmental aggressors, such as pollutants, UV radiation, or pathogens. Such sort of a safeguard on the body is necessary to maintain the integrity of the skin to prevent damage.
While it is helpful in deeper penetration and skin hydration, LMW-HA does not offer comparable superficial protection. It assists in the repair and regeneration of the skin from deeper within without offering the superficial protective advantages of HMW-HA.
Safety and Stability
Due to the large biocompatibility and stability, the compatibility of HMW-HA is very high with a broad range of uses and barely brings a risk of adverse reactions. Its great molecular size somewhat mimics the naturally occurring HA in vivo, reducing the likelihood of immune rejection or sensitivity. This hence makes it highly appropriate for use in the long term for skincare or medical procedures.
LMW-HA is also biocompatible, yet it can be very prone to fast degradation and, hence, may need effective stabilization in formulations to ensure its prolonged efficacy. Due to the smaller size, it is easily absorbed and metabolized much faster, leading to more frequent applications.
Extended Efficacy
HMW-HA is biologically active on the skin or within tissues for extended periods of time, primarily due to its large molecular structure. This long activity translates to a durable effect in moisturizing, lubricating, and protecting of the skin and mucous membranes, hence useful in products and treatments with long-term benefits.
On the other hand, LMW-HA gives faster penetration and quicker results but might need to be replenished more frequently because of fast absorption and degradation.
High vs low molecular weight hyaluronic acid: Comparative Applications
Skincare
- HMW-HA: Ideal for use in moisturizers, masks, and protective creams where surface hydration and barrier protection are critical. It is often included in formulations aimed at providing long-lasting moisture and reducing transepidermal water loss.
- LMW-HA: Best suited for serums, essences, and deep-penetrating treatments where the goal is to deliver hydration deep into the skin layers and promote cellular repair and regeneration.
Medical Treatments
- HMW-HA: Widely used in joint injections for osteoarthritis to provide lubrication and reduce inflammation. It is also employed in wound care products to promote healing and reduce scar formation.
- LMW-HA: Utilized in treatments requiring deep tissue repair, such as dermal fillers for skin rejuvenation and products aimed at enhancing tissue regeneration and repair.
Ophthalmology
- HMW-HA: Used in artificial tears and as a viscoelastic agent in eye surgeries to protect and lubricate the ocular surface, ensuring smooth movements and reducing irritation.
- LMW-HA: May be included in eye drops aimed at delivering hydration to the deeper layers of the eye’s surface, but its use is less common due to lower viscosity and protective properties.
Nutrition and Supplements
- HMW-HA: Incorporated into dietary supplements and functional beverages to support joint health and skin hydration. Its larger molecular size ensures sustained release and prolonged benefits.
- LMW-HA: Used in supplements designed for enhanced absorption and bioavailability, targeting deep tissue hydration and repair from within.
Conclusion
High molecular weight hyaluronic acid (HMW-HA) and low molecular weight hyaluronic acid (LMW-HA) both play vital roles in various applications, each offering distinct benefits based on their unique properties. HMW-HA excels in providing long-lasting surface hydration, lubrication, anti-inflammatory effects, and protection, making it indispensable in skincare, medical treatments, and ophthalmic solutions. In contrast, LMW-HA is valuable for its deep penetration, hydration, and tissue repair capabilities.
Understanding the differences between these two forms of HA allows for more targeted and effective use in products and treatments, maximizing their respective advantages to meet specific needs and objectives. As research and technology continue to advance, the complementary use of both HMW-HA and LMW-HA will likely lead to even more innovative and effective solutions in health, beauty, and wellness.
Stanford Chemical Company (SCC) is a premium supplier of hyaluronic acid, offering sodium hyaluronate powders in a variety of molecular weights. For more information or specific applications, please visit our home page.
