
Hyaluronic acid is a natural moisturizing and lubricating agent, widely used in fields like medicine, food, skincare, and medical aesthetics. As its market continues to grow, counterfeit and low-quality products sometimes appear. So, how can buyers distinguish the real from the fake?
If you are a purchaser responsible for acquiring hyaluronic acid raw materials for your company or research institute, there are several ways to detect and judge its authenticity.
1. Component Testing and Analysis
1.1 Third-party Testing Reports
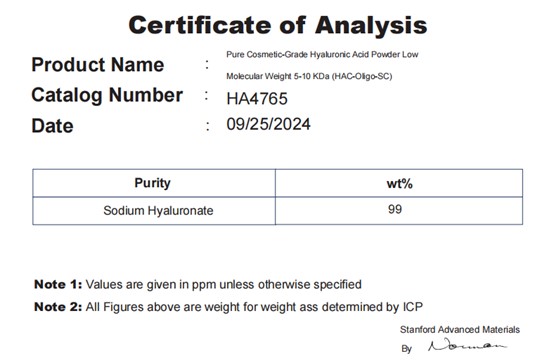
By asking suppliers for test reports from independent third-party laboratories, you can verify the purity, molecular weight range, and compliance with industry standards of the sodium hyaluronate. Legitimate products usually come with a Certificate of Analysis (COA) or other related reports.
For example, here is a COA for one of our products: Pure Cosmetic-Grade Hyaluronic Acid Powder Low Molecular Weight 5-10 KDa (HAF-Oligo-SC).
1.2 HPLC Testing (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography)
HPLC testing is one of the common methods to determine the purity of sodium hyaluronate. This test analyzes the molecular structure of the sample and checks for impurities. The peak chart should match the standard, and the presence of extra peaks could indicate adulteration.
1.3 Molecular Weight Range Testing
The molecular weight of sodium hyaluronate affects its effectiveness in various applications. You can verify if the molecular weight meets product specifications (e.g., 100kDa-2000kDa) using Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC). Discrepancies in molecular weight may indicate substandard or adulterated products.
2. Appearance and Physical Characteristics Tests
2.1 Visual Inspection
High-quality sodium hyaluronate powder is generally white or slightly yellowish, fine, and odorless. Significant color deviations like gray or black, or any strange odor, may suggest impurities or poor storage conditions.

2.2 Solubility Test
Dissolve the sodium hyaluronate powder in purified water and observe its dissolution speed and the clarity of the solution. Genuine sodium hyaluronate should dissolve quickly, forming a transparent and slightly viscous solution. Cloudiness or precipitation may indicate impurities.
2.3 Dissolution Time and Viscosity Test
When dissolved, sodium hyaluronate forms a characteristic gel-like viscosity. You can measure the dissolution time and viscosity at specific concentrations. If the solution is too thin or lacks significant viscosity, it might indicate low-quality or adulterated raw materials.
3. Supplier Qualification and Production Process Review
3.1 Review Supplier Credentials
Choose suppliers with good reputations and certifications. Factories certified by GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) or ISO (International Organization for Standardization) are usually more reliable and reduce the risk of adulteration.
For example, the factories where our products are made have obtained relevant certifications, which shows the safety of the products.
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management System)
- ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System)
- ISO 22000 (Food Safety Management System)
Note: ISO sets standards, and certification bodies such as QAC are responsible for evaluating whether companies meet these standards and issuing corresponding certifications.
3.2 Production Process Transparency
Sodium hyaluronate is typically produced via microbial fermentation (such as using streptococcus). High-quality manufacturers should provide detailed descriptions of their production processes and openly share their quality control measures, such as sterile operations and impurity removal.
4. Laboratory Testing Tools and Methods
4.1 Moisture Content Testing
Use Karl Fischer titration to detect the moisture content of the sample. High-purity sodium hyaluronate should have a moisture content below 1%. High moisture content may suggest poor storage or adulteration.
4.2 Heavy Metal Content Testing
Sodium hyaluronate powder may contain trace amounts of heavy metals. Testing with ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) ensures that heavy metals like lead and mercury are within safe limits.
4.3 Protein Impurity Testing
Protein residues may be present in sodium hyaluronate, especially if it is extracted from animal tissue. Using colorimetric or BCA (Bicinchoninic Acid Assay) methods, you can check if the protein impurities are within acceptable limits.
5. Storage Conditions and Packaging Review
5.1 Packaging and Storage Environment
Sodium hyaluronate is hygroscopic, so the packaging should be sealed and moisture-proof. The packaging should clearly indicate production dates, batch numbers, and storage conditions. Exposure to high humidity and temperature can degrade the product.
5.2 Anti-counterfeiting Labels and Traceability
Products from legitimate suppliers should have clear labels, batch numbers, and anti-counterfeiting features. These labels allow you to trace the production date, origin, and relevant certifications, ensuring the authenticity of the raw material.
