
Hyaluronic acid (HA) plays a significant role in various medical treatments because of its unique properties. Here are some key applications and their specific functions:
1. Revitalizing Joints: The Power of Hyaluronic Acid Therapy
Hyaluronic acid is commonly used to treat joint diseases such as osteoarthritis. When injected into the joint, it acts as a lubricant and shock absorber, reducing pain and improving joint function. This treatment is known as hyaluronic acid joint injection or viscosupplementation.
Studies have shown that hyaluronic acid injections significantly improve the quality of life for patients with knee osteoarthritis.
How Hyaluronic Acid Treats Joint Diseases
- Lubrication: Hyaluronic acid acts as a lubricant in the synovial fluid of joints. It helps to reduce friction between the articular cartilage of synovial joints during movement, which can be significantly beneficial for osteoarthritis patients.
- Shock Absorption: HA provides a cushioning effect in the joints, absorbing mechanical shocks and protecting the joints during physical activities.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: HA has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, reducing the levels of inflammatory mediators and enzymes that degrade cartilage.
- Pain Relief: By improving the viscosity and elasticity of the synovial fluid, HA injections can alleviate pain associated with joint movement.
- Cartilage Protection: HA may help to protect the cartilage by enhancing the production of cartilage matrix components and inhibiting cartilage-degrading enzymes.
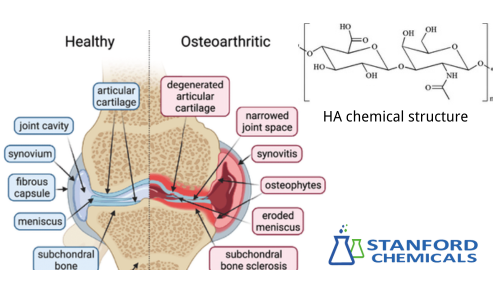
Fig 1. How Hyaluronic Acid Treats Joint Diseases[1]
Side Effects of Hyaluronic Acid
Mild side effects can include temporary pain at the injection site, swelling, and stiffness. These are usually transient and resolve on their own. Rarely, some patients may experience allergic reactions to HA. It is important to inform the healthcare provider of any allergies or previous reactions to similar treatments.
2. Hyaluronic Acid: Essential for Optimal Eye Health
Hyaluronic acid (HA) plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving eye health due to its unique viscoelastic properties and biocompatibility.
Cataract Surgery
During cataract surgery, hyaluronic acid is used as a viscoelastic substance to protect the delicate structures of the eye:
Corneal Transplantation
Hyaluronic acid is used in corneal transplantation to enhance the surgical outcome. HA solutions are used to store and preserve donor corneas, ensuring tissue viability until transplantation. Furthermore, during the procedure, HA provides lubrication and protection.
Dry Eye Syndrome
Hyaluronic acid is a key ingredient in many artificial tears and eye drops used to treat dry eye syndrome. Because HA retains moisture on the ocular surface and provides long-lasting hydration and relief from dryness.
Refractive Surgery
In procedures such as LASIK and PRK, hyaluronic acid aids in postoperative recovery.
Maybe you are interested: What Does Hyaluronic Acid Do to Your Eyes?
3. Hyaluronic Acid: Your Ally in Maintaining Oral Health
In dentistry, hyaluronic acid is used to treat periodontal disease and oral ulcers. Its anti-inflammatory and tissue regeneration properties help accelerate the healing process.
The application of hyaluronic acid in periodontal disease treatment shows significant efficacy, reducing inflammation and promoting gum health.
How Hyaluronic Acid Protects Oral Health
Treatment of Periodontal Disease
HA reduces inflammation in the gums, helping to mitigate the progression of periodontal disease. In addition, it promotes the healing of periodontal tissues by stimulating cell migration and proliferation, enhancing tissue regeneration and repair.
Management of Oral Ulcers
HA is effective in the treatment of oral ulcers, such as aphthous stomatitis. HA can form a protective barrier over ulcers, providing pain relief and reducing discomfort.
Support in Dental Surgeries
HA can be applied post-surgery to enhance wound healing and reduce recovery time. Its application helps in minimizing inflammation and promoting faster tissue regeneration.
4. Hyaluronic Acid: The Secret to Skin Repair and Aesthetic Beauty
Hyaluronic acid is widely used in skincare and cosmetic medicine due to its powerful moisturizing and repair capabilities. It is used as a dermal filler to reduce wrinkles and facial hollows and promotes wound healing and burns treatment.
More information: Hyaluronic Acid vs. Retinol vs. Vitamin C: Which Is Best for Skincare
5. The Healing Power of Hyaluronic Acid in Surgery and Trauma
Hyaluronic acid is often used in plastic surgery and trauma repair, such as repairing soft tissue defects and improving scar quality. Its biocompatibility and ability to promote cell migration and proliferation make it an ideal biomaterial.
The use of hyaluronic acid in trauma repair significantly shortens healing time and improves tissue repair quality.
How Hyaluronic Acid Promotes Wound Healing
Hydration and Moisture Retention
A moist wound environment can facilitate better tissue repair and regeneration. And then reduce the risk of scar formation.
Anti-inflammatory Properties
HA helps to modulate the inflammatory response, reducing excessive inflammation that can hinder the healing process.
Promotion of Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is a critical part of the wound-healing process. HA provides a scaffold that supports the growth of new blood vessels into the wound area, ensuring adequate oxygen and nutrient supply for healing tissues.
More information: Medical Grade Hyaluronic Acid and Wound Healing
Conclusion
The importance of hyaluronic acid in medical treatments stems from its unique biological properties, such as high viscoelasticity, good biocompatibility, and strong moisturizing ability. These characteristics make it widely applicable in joint disease treatment, ophthalmic surgery, skin repair, cosmetic medicine, oral health, and trauma repair, significantly improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
[1] [1] Fig 1. Anatomy of the healthy and osteoarthritic knee joint. Created via canvas. Source: Smith, Abbi & Sigurbjörnsdóttir. (2022). Hedgehog signaling in bone and osteoarthritis: the role of Smoothened and cholesterol. The FEBS Journal. 290. 10.1111/febs.16440.
